


|

|

|
| Next Lecture | Last Lecture | UWS | Physics Dept |
| Brightness | Apparant Magnitude |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0 |
| 1/2.514 | +1.0 |
| 1/2.5142 | +2.0 |
| 1/2.5143 | +3.0 |
| 1/2.5144 | +4.0 |
| 1/2.5145=1/100=10-2 | +5.0 |
| 10-4 | +10.0 |
| 10-6 | +15.0 |
| 10-8 | +20.0 |
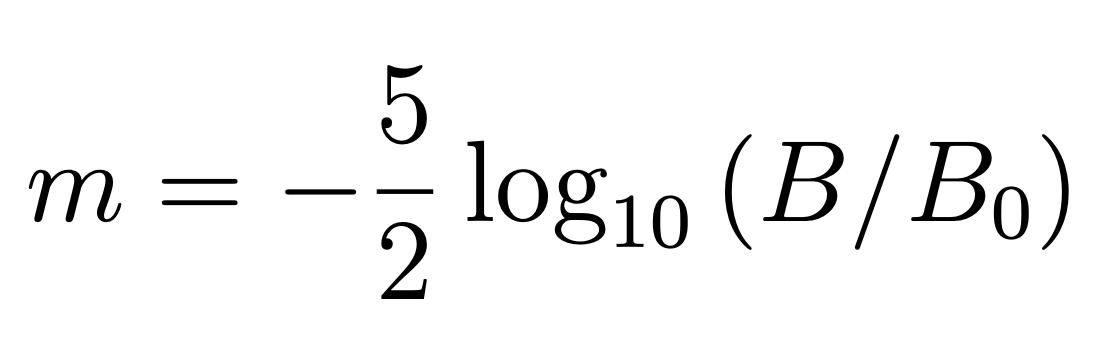 Note that B has a technical meaning which I wont give here.
Note that B has a technical meaning which I wont give here.
The absolute magnitude scale is what we need to compare stars. To calculate it we need a stars apparant magnitude and distance from us.
We compute the absolute magnitude, M, from the apparant magnitude, m, and the distance (in parsecs), DL , using
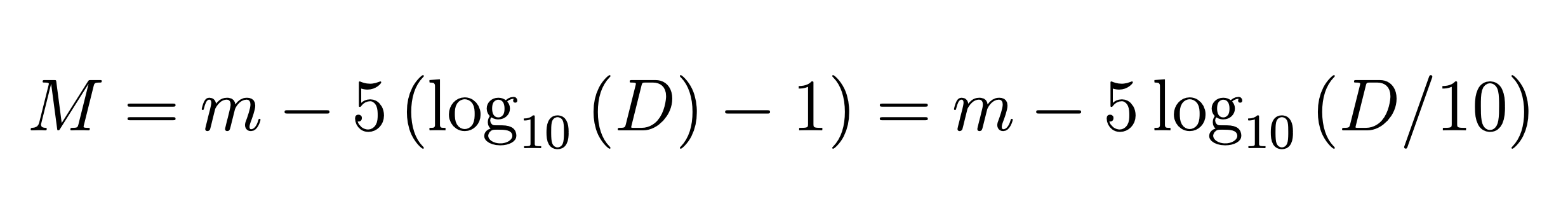
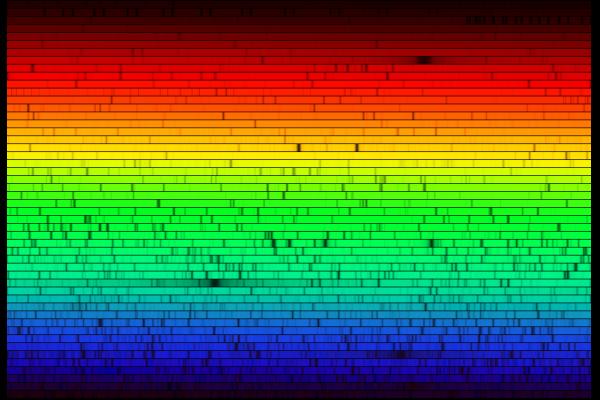
Light is a Wave It is a wave of the electric and magnetic fields. The different type of light can be characterised by the wavelength - the distance between peaks of the waves. In order of decreasing wavelength the type of light include, Radio waves, microwave, infra-red, red visable light, blue visable light, ultra-violet, x-rays, .. White light is a mixture of all wavelengths. Splitting light into the different wavelengths is enormously important in Astronomy.
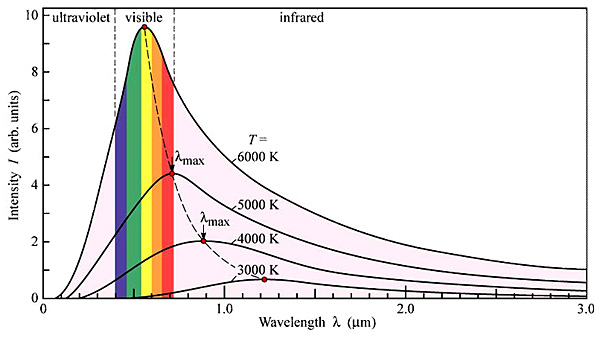
Hot objects emit
light
in all wavelengths. However the "profile" of wavelengths changes as the
object's temperature increases. At low
T's the object will mainly radiate in the infra-red. As the temperature
is increased the object emits more total light and the profile changes -
shorter wavelengths become more dominant. As T increases the object
appear red - it is red-hot. If T increases further the object is
brighter and the colour shifts towards white. Further temperature
increases make the light have a blue tinge. It is important that we can
look at a stars colour and decide its temperature.
| Temperature | Maximum Wavelength | Corresponding type of light |
|---|---|---|
| 290K | 0.001 cm | Infrared |
| 1000K | 0.00029 | Infrared |
| 5800 | 0.00005 | Visable |
| 10,000 | 0.000029 | Ultraviolet |
| 1,000,000 | 0.00000029 | X-rays |
| Spectral Type | Colour | T (C) | Examples | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | Blue-Violet | 28,000-50,000 | Mintaka (delta-Ori) | |
| B | Blue-White | 10,000-28,000 | Rigel | |
| A | White | 7,500-10,000 | Sirius | |
| F | Yellow-White | 6,000-7,500 | Procyon | |
| G | Yellow | 5,000-6,000 | Sun | |
| K | Orange | 3,500-5,000 | Albebaron | |
| M | Red-Orange | 2,500-3,500 | Betalguese | |
© Dave Dunbar 2020