



|

|

|
| Next Lecture | Last Lecture | Canvas | UWS | Physics Dept |

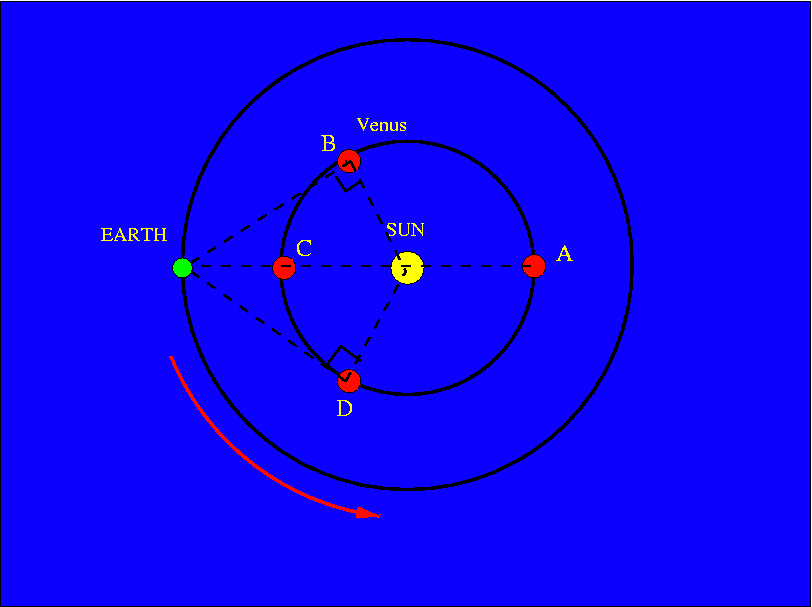
| Greatest Eastern Elongation | Conjunction | Greatest Western Elongation | Conjunction |
| June 6th 2015 | Aug 15th 2015 | Oct 26th 2015, | Jun 6th 2016 |
| Jan 12th 2017 | Mar 25th 2017 | Jun 3rd 2017, | Jan 9th 2018 |
| Aug 17th 2018 | Oct 26th 2018 | Jan 6th 2019, | Aug 14th 2019 |
| Mar 24th 2020 | May 13th 2020 | Aug 13th 2020 | Mar 26th 2021 |
| Oct 29th 2021 |
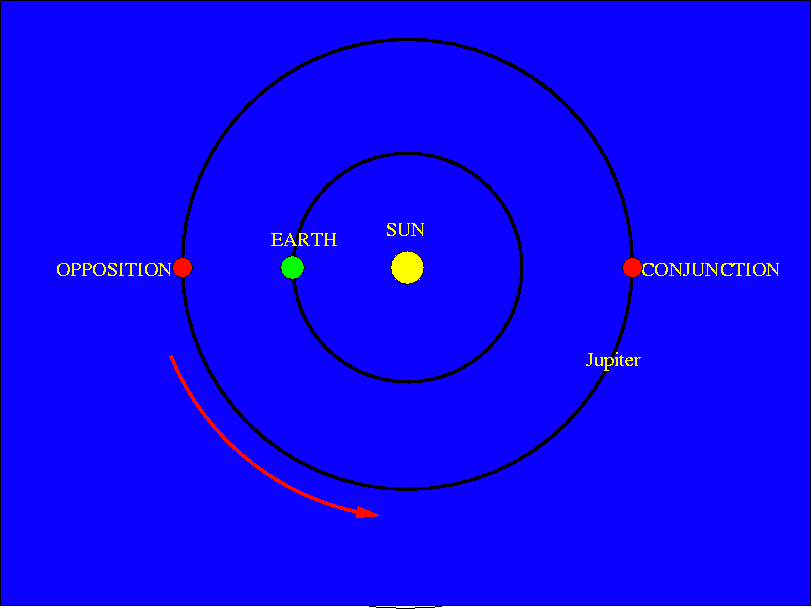
| Mars | Jupiter | Saturn |
| Oct 29th 2011 | Apr 4th 2011 | |
| Apr 8th 2014 | Jan 5th 2014 | May 10th 2014 |
| - | Feb 5th 2015 | May 23rd 2015 |
| May 22nd 2016 - | Mar 8th 2016 | June 3rd 2016 |
| - | Apr 7th 2017 | June 15th 2017 |
| 27th July 2018 | May 9th 2018 | June 27th 2018 |
| - | June 10th 2019 | July 9th 2019 |
| Oct 13th 2020 | July 14th 2020 | July 20th 2020 |