Observations and the Solar System : Lecture 4
Galileo
Galileo Galilei did not invent the telescope but was the first to use
it to observe the heavens. He unveiled a large number of facts -
strongly supporting the Copernican view. He was under
"vehement suspicion of heresy" and placed under house
arrest for the remainder of his life.
Among his notable discoveries were
- Craters and mountains on the moon
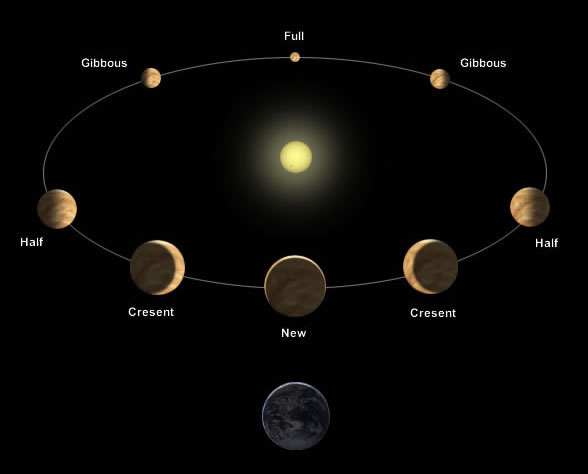
- Venus has phases - like the moon. The observed pattern
was that expected from the heliocentric viewpoint.
- He discovered that around Jupiter there
were 4 moons .
Gravitation and Newton (1642-1727)
Isaac Newton changed astronomy and physics entirely. Kepler's three
laws are a description of nature. Newton introduced a theory
of Gravitation which explained nature.
F = ma
F= Gm1m2 /R2
The second equation describes the attractive force between
two massive objects. Ignoring the maths, Keplers three laws follow
logically from these two equations. Consequently the dynamics
of the solar system have been well understood.
Uranus, Neptune and Pluto
We discussed how the last three planets were discovered,
Uranus was discovered in 1781 (by Hershall) by accident
Neptune was predicted from the observed anomalies in the motion of
Uranus by Adams and Le Verrier. Uranus orbit seemed
not to satisfy Keplers second law (equal area in equal time).
Possible explainations were
- Faulty Observations
- Corrections to Newtons Theory of Gravity
- An unknown planet speeding up Uranus in positon B and slowing it down in position A
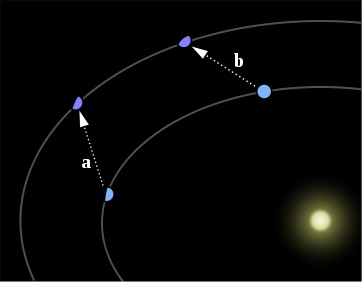
Le Verrier and Adams predicted where this extra planet would be and indeed
it was observed.
A great triumph for science!
After observing Neptune orbits there were also some possible
anomalies. This led to seculation regarding a Planet X.
Pluto was discovered by extensive searches for planet X. Pluto however
is far too small (and in the wrong place) to eplain the anomalies.
© Dave Dunbar 2020